Your cart is currently empty!
Category: Health and Safety Guides
Dive into our comprehensive Health and Safety Guides—your one-stop resource for step-by-step safety procedures, risk assessment methodologies, audit-ready checklists, and best practices. Whether you’re building a safety management system from scratch or updating existing policies, you’ll find clear, actionable guidance and expert insights to keep your workplace compliant, protect your people, and minimize legal exposure.
-
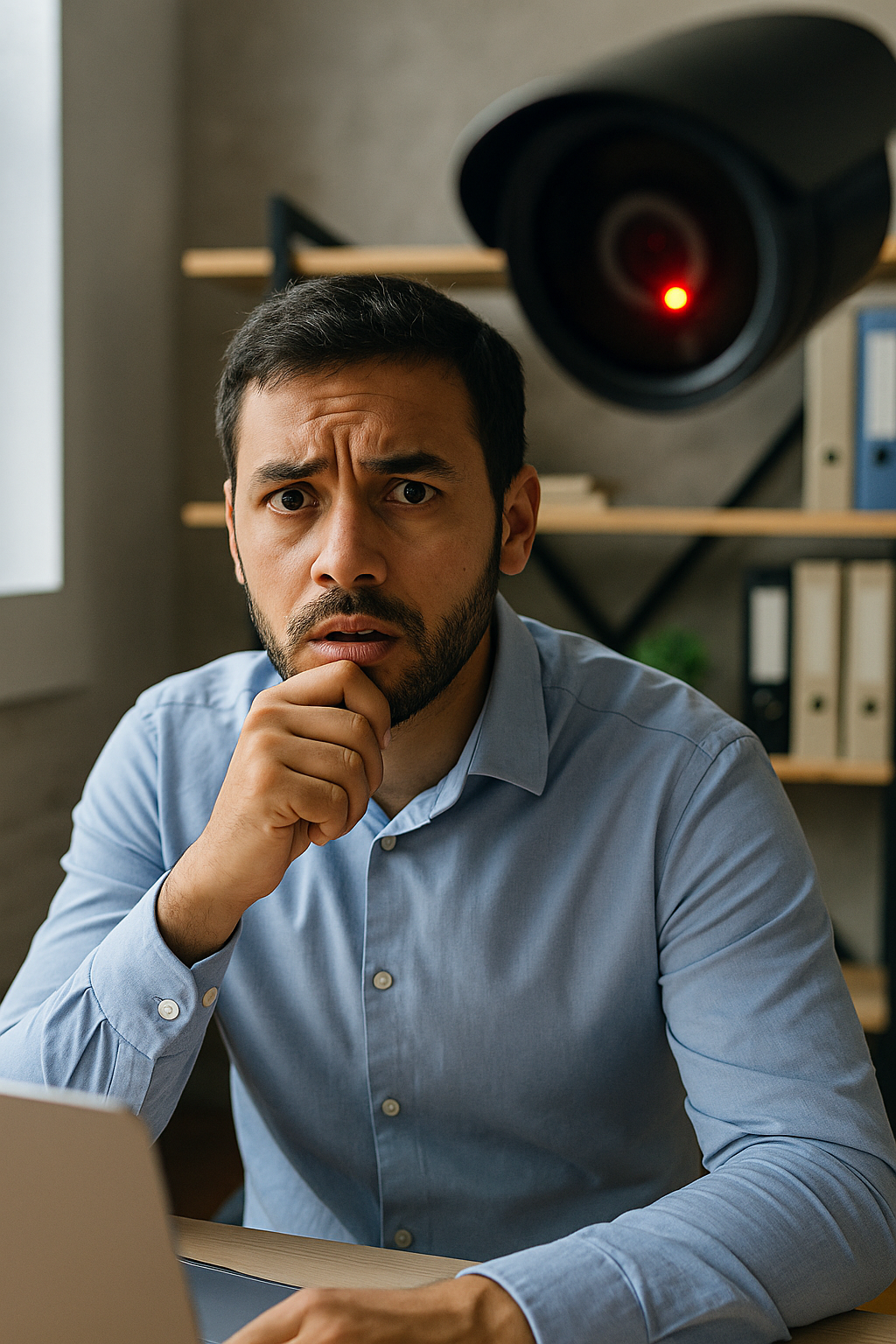

Bossware or Beware? How Workplace Surveillance Is Silently Fueling the Mental Health Crisis
In an era where hybrid work and digital productivity tools are the norm, a new kind of safety concern is quietly emerging in UK workplaces: bossware.
Sold as a tool to monitor productivity, enforce accountability, and ensure worker safety, bossware is surveillance software that tracks your every move—from keystrokes and mouse activity to webcam feeds and idle time alerts. While it may help employers feel in control, it’s contributing to something far more dangerous: a silent epidemic of workplace stress and anxiety.
What Is Bossware?
Bossware refers to employee-monitoring software used to track digital activity. Common features include:
- Keystroke logging
- Mouse movement tracking
- Screen and webcam recording
- Productivity scoring and idle time alerts
- GPS tracking (especially in delivery and logistics roles)
- Email and communication monitoring
It’s often used without explicit employee consent or is buried in vague policy language, especially in remote or hybrid work settings where supervision is perceived as difficult.
A 2024 survey by Prospect Union revealed that 52% of remote workers in the UK were concerned about employer surveillance. Among younger workers (aged 18–34), that number rose to 60% (Prospect, 2024).
The Mental Health Fallout: A Statistical Breakdown
The UK’s Health and Safety Executive (HSE) 2023/24 statistics revealed:
- 1.7 million people suffered from work-related ill health
- Of these, 776,000 cases were due to stress, depression or anxiety
- Mental health-related issues made up 45% of all work-related illness
- An estimated 33.7 million working days were lost due to stress, depression or anxiety
- 57% of all sickness absence in 2023/24 was mental health-related (HSE, 2024)
Separate research from the Trades Union Congress (TUC) in late 2023 showed:
- 1 in 5 workers say surveillance tech has increased their stress levels
- 1 in 3 feel pressured to stay online outside working hours due to monitoring tools
- 42% of workers in jobs with surveillance software say they are less likely to take breaks (TUC, 2023)
Additionally, The Guardian reported that AI-driven bossware is now being implemented in customer service and retail sectors at increasing rates, raising ethical concerns about constant monitoring and algorithmic bias (The Guardian, March 2025).
All of these findings point to a growing psychosocial hazard: digital over-monitoring.
Real Stories From the Monitored Frontlines
Zara, Customer Support Agent (Remote)
Zara worked from home but was expected to stay logged into five systems with her webcam on throughout the shift. When her cat knocked over a cup of water during a call and she briefly stepped away, her “productivity score” dropped, triggering a performance warning.
“It felt like I was being watched by a machine that didn’t care if I was human,” she said. She resigned four months later due to stress and sleep issues.
Abdul, Delivery Dispatcher
Abdul’s company implemented keystroke logging to “streamline workflows.” It led to constant performance reviews based on system metrics, not actual team feedback. He reported daily anxiety and chest tightness.
“Even when I did good work, I felt like I was failing. I couldn’t relax. Ever.”
Claire, Legal Assistant
Claire was unaware her emails were being monitored until she received a formal HR warning about her “tone” in internal correspondence. The issue stemmed from AI-based sentiment analysis. “I felt humiliated and paranoid after that,” she said. “Every message became a source of fear.”
The Psychological Hazards of Surveillance
Workplace surveillance may not cause physical harm, but its psychological impact is well documented:
- Loss of Autonomy: Constant tracking removes a sense of control and increases perceived helplessness
- Hypervigilance: Workers operate in constant fear of being flagged as unproductive
- Emotional Exhaustion: Surveillance increases mental fatigue and reduces capacity to recover
- Dehumanisation: Employees feel more like data points or risk scores than people
- Presenteeism: Workers stay online or work through illness just to appear productive
A 2023 CIPD report found that 76% of employees who felt monitored at work were also likely to report moderate to high stress levels (CIPD, 2023).
Bossware in Practice: Industries Under Watch
Logistics & Warehousing
- GPS, time-on-task dashboards, and wearable trackers are common
- Amazon UK alone reported 119 serious injuries between 2019 and 2024 at its sites despite high-tech safety tools (Financial Times, 2024)
Call Centres & Customer Service
- Webcam monitoring, keystroke tracking, and sentiment analysis dominate
- Workers in this sector have among the highest reported rates of anxiety per HSE data
Remote and Hybrid Office Work
- 48% of remote workers report being monitored via software
- 27% of those say it has negatively affected their wellbeing
Legal and Ethical Considerations in the UK
UK employers must:
- Conduct impact assessments before deploying surveillance tech
- Provide transparency about monitoring tools under the Data Protection Act 2018
- Include digital wellbeing in their stress risk assessments as required under HSE guidance
Failure to do so can result in claims under:
- Health and Safety at Work Act 1974
- Employment Rights Act 1996
- GDPR / UK Data Protection Law
What Employers Should Do Instead
- Co-create surveillance policies with employee input
- Limit monitoring to essential safety functions
- Invest in psychological safety training for managers
- Embed digital wellbeing in your health and safety management system
- Offer mental health support alongside any performance tools
Final Thoughts: Surveillance Is Not a Substitute for Safety
Bossware may give the illusion of control, but it quietly erodes trust, motivation, and mental health. Real safety requires more than productivity dashboards — it demands compassion, boundaries, and open dialogue.
As more workers speak up about feeling watched instead of supported, UK companies must ask:
Are we managing risk – or just managing optics?
-

4 Best Stove Guards to Keep Toddlers Safe in the Kitchen – From Budget Shields to Smart Protection
Every year, thousands of children suffer painful burns from kitchen accidents. The good news? You can prevent most of them with a simple stove guard — starting at just £25.
Whether you’re baby-proofing for a toddler or protecting a curious preschooler, these are the best Stove Guards for Toddlers UK.
👶 Why Every Parent Needs a Stove Guard
Did you know:
- Over 7,000 UK children are treated for kitchen burns every year – most from grabbing a hot pan or touching a hob.
- Burn injuries are one of the top reasons toddlers are rushed to A&E.
- These accidents happen in seconds — often when a parent turns away for just a moment.
Stove guards are specially designed to block children from reaching hot pots, turning knobs, or touching dangerous surfaces. Some even come with smart technology that can shut off the cooker automatically if left on.
🏆 Top 4 Best Stove Guards for Toddlers UK in 2025
Product Best For Type Price bremermann Stove Guard Budget childproofing Acrylic barrier £25 Fred Safety Hob Guard Stylish family kitchens Designer shield £69 Lakeland Induction Mat Surface burn prevention Silicone mat £25 Firechief FSW1 Elderly & families Smart auto cut-off £366
🔒 1. bremermann Stove Guard – Best Budget Stove Guard for Toddlers

💷 Price: ~£25
🛠 Type: Clear acrylic barrier
⭐ Amazon Rating: ★★★★☆ (4.0)✅ Why It’s Great for Kids:
This simple barrier attaches around the hob to prevent toddlers from reaching hot pots or burners. It’s perfect for parents looking to baby-proof on a budget without drilling or complex installation.
🔍 Pros:
- Inexpensive and effective
- Easy to install (no tools needed)
- Heat-resistant plastic
- Works on most standard hobs
❌ Cons:
- No protection from fire risk
- May not fit large or uniquely shaped hobs
Ideal for: Parents of crawling babies or toddlers aged 1–4.
👶 2. Fred Safety Stove & Hob Guard – Best for Stylish, Family-Friendly Homes

💷 Price: ~£69
🛠 Type: Designer acrylic shield
⭐ Reviews: High brand trust (newer product)✅ Why It’s Great for Kids:
Created by child safety experts, this hob guard combines safety with aesthetics. It’s designed to block your child from hot pots while blending into modern kitchens.
🔍 Pros:
- Sleek, modern design
- Easy to mount and remove
- Designed for families with toddlers
- Non-intrusive and clean look
❌ Cons:
- More expensive than basic guards
- No heat-sensor or fire prevention
Ideal for: Parents who care about both design and childproofing.
🧽 3. Lakeland Induction Hob Protector – Best for Induction Hob Safety
💷 Price: ~£25
🛠 Type: Silicone mat for induction hobs
⭐ Amazon Rating: ★★★★☆ (3.8)✅ Why It’s Great for Kids:
While this isn’t a barrier guard, it prevents burns from touching hot hob surfaces, which is especially useful for toddlers exploring countertops.
🔍 Pros:
- Protects surfaces and hands
- Reduces post-cooking heat
- Easy to clean and reusable
- Cut-to-fit design
❌ Cons:
- Doesn’t block pans or knobs
- Not suitable for gas hobs
Ideal for: Parents with induction cookers and toddlers who love to touch everything.
🚨 4. Firechief FSW1 Smart Stove Guard – Best for Busy Households or Carers
💷 Price: ~£366
🛠 Type: Smart sensor + power cut-off
⭐ Rating: ★★★★☆ (4.0)
📜 Safety Certified: EN 50615✅ Why It’s Great for Kids:
This smart device detects overheating or unattended cooking and automatically shuts off the stove. While it doesn’t block physical access, it provides peace of mind when kids are around and you’re distracted or multitasking.
🔍 Pros:
- Prevents fires with heat detection
- Alerts before risk escalates
- Fully automatic shut-off
- Certified safety tech
❌ Cons:
- High cost
- Electric stoves only
- Professional installation needed
Ideal for: Parents, carers, or grandparents who want tech-driven safety.
🧾 Final Thoughts: Which best Stove Guards for Toddlers UK Is Right for Your Child’s Safety?
- Best Budget Option: bremermann – effective and affordable
- Best for Style + Function: Fred Safety – modern design, family-focused
- Best for Induction Hobs: Lakeland – great surface protector
- Best All-Round Smart Choice: Firechief FSW1 – trusted and reliable
📝 Bonus Tips for Kitchen Child Safety:
- Install knob covers to stop toddlers from turning on burners
- Keep handles turned inward when cooking
- Never leave a toddler alone in the kitchen — even for a minute
- Add a baby gate if your kitchen is open-plan
👶 At £25 you can get one of the best Stove Guards for Toddlers UK and can protect your child from years of pain and trauma.
Don’t wait for an accident — install before the “what if” becomes real. -

Top 5 Home Safety Products in the UK You Need in 2025
Looking for the best home safety products in the UK for 2025? You’re in the right place.
Every year, thousands of household injuries and emergencies could be prevented with just a few low-cost tools. From fire safety to bathroom falls, carbon monoxide poisoning to childproofing hazards, most risks are avoidable — if you’re prepared.
At Safe-Comply.com, we help people take simple, sensible steps to live safer. Here’s our expert guide to the top 5 home safety devices in the UK for 2025 — handpicked for reliability, affordability, and ease of use.
🔥 1. Kidde 10SCO Smoke & Carbon Monoxide Combo Alarm

💰 Price: Approx. £21.82
⭐ Rating: 4.5/5 (1,400+ reviews)
📦 Buy on Amazon UK »Full Review:
This dual-sensor alarm from Kidde is a best-in-class device trusted in homes across the UK. It combines photoelectric smoke detection with carbon monoxide sensing, so you only need one device per room — saving space and hassle.
The standout feature is the sealed 10-year battery, which means you won’t need to replace batteries or hear annoying low-battery beeps in the middle of the night. It’s completely maintenance-free apart from the occasional test.
The photoelectric sensor responds faster to slow-burning fires (like smouldering upholstery or wiring), and it’s much less prone to false alarms from cooking — a common frustration with cheaper detectors.
The alarm is loud (85 dB), and the LED indicators let you know whether the alert is due to smoke or carbon monoxide. It also has a hush/test button on the front that’s easy to press.
Pros:
- 2-in-1 protection in a single device
- 10-year sealed lithium battery
- Reliable brand and UK certified
- Minimal false alarms
Cons:
- No smartphone alerts or smart home integration
- Slightly more expensive than basic models (but lasts longer)
Best for: Anyone wanting dependable, long-term protection from two of the deadliest home risks — smoke and carbon monoxide.
🧯 2. StaySafe All-in-1 Fire Extinguisher (5-Pack)

💰 Price: Approx. £19.99
⭐ Rating: 4.9/5
📦 Buy on Amazon UK »Full Review:
Most UK homes don’t have a fire extinguisher, and that’s a serious oversight. Fires in kitchens, garages, and even cars are more common than we like to admit. The StaySafe All-in-1 fire extinguisher pack is a smart and cost-effective way to fix that.
This 5-pack includes compact ABC-rated extinguishers that cover:
- A: wood, paper, cloth
- B: flammable liquids like cooking oil or petrol
- C: electrical fires
Each extinguisher is lightweight and comes with a wall-mounting bracket. They’re designed to be easy to grab and use quickly, even in a panic situation. Because they’re dry powder units, you don’t need to worry about water damage to electronics or appliances.
The size makes them ideal for smaller spaces — keep one in the kitchen, one in the garage, one in the car, and two as backup.
Pros:
- Covers all common household fire types
- Space-saving and lightweight
- Great value for money
- Simple operation — no training needed
Cons:
- Not suitable for large fires (intended for small incidents)
- Must be replaced once discharged
Best for: Homeowners and renters who want convenient, multi-location fire protection at a budget-friendly price.
🚼 3. 12-Pack Child Safety Cabinet Locks

💰 Price: Approx. £8.40
📦 Buy on Amazon UK »Full Review:
Young children are naturally curious — and that curiosity can be dangerous when they open drawers filled with knives, cleaning products, or medicines. These adhesive child safety locks offer an easy, drill-free way to childproof your home.
This 12-pack gives you enough to secure the most high-risk areas of your home: kitchen cabinets, bathroom drawers, fridge doors, or even toilet lids. Installation is fast — peel the adhesive backing and stick the locks in place. No tools needed.
The flexible design means they fit both flat surfaces and corners, and they’re easy for adults to unlock but very tricky for kids.
They don’t damage surfaces, so they’re perfect for renters who need a temporary but effective safety solution.
Pros:
- Easy to install and remove
- Reusable and adjustable
- No tools or drilling required
- Strong adhesive and durable build
Cons:
- Adhesive can weaken over time (check regularly)
- Not ideal for extremely heavy drawers
Best for: Parents, grandparents, and anyone childproofing their home without permanent hardware.
🚑 4. Rennington BS8599-1 First Aid Kit (HSE Compliant)
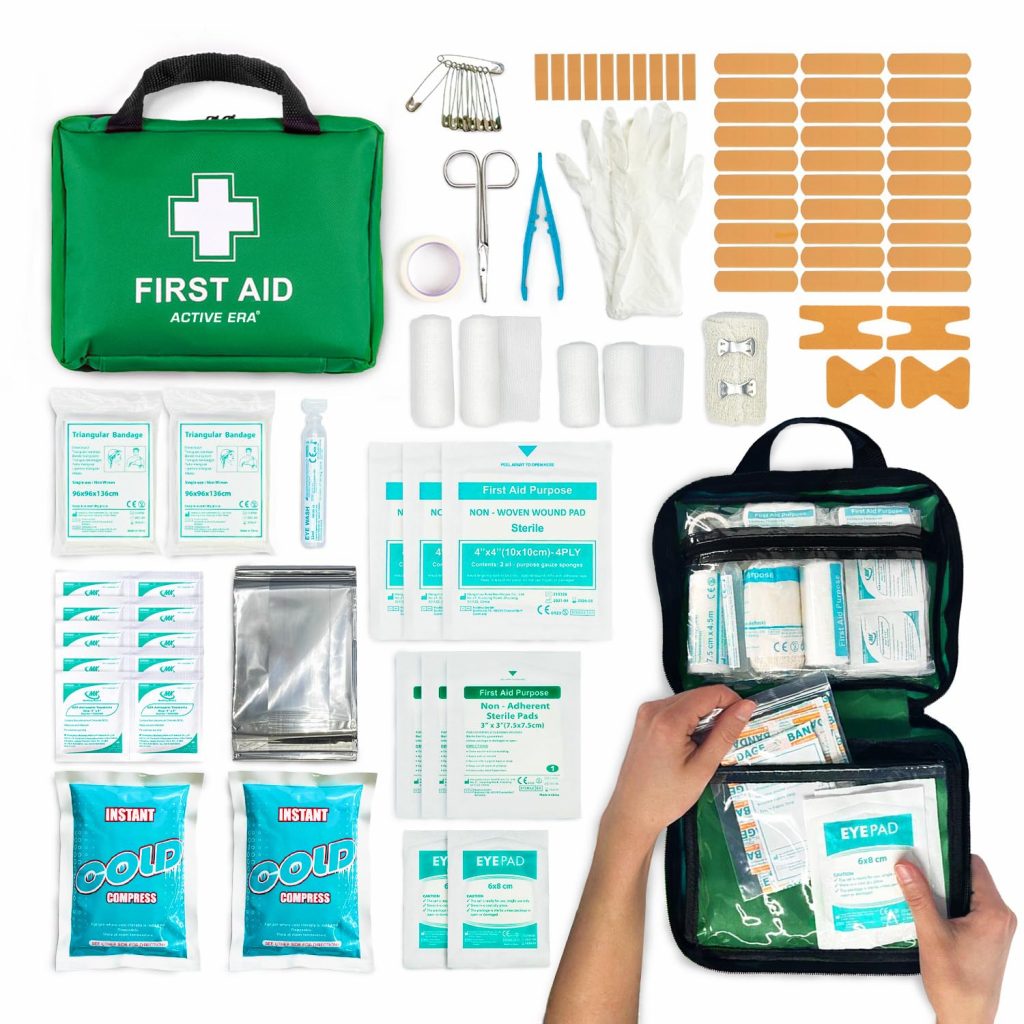
💰 Price: Approx. £23.95
⭐ Rating: 4.7/5
📦 Buy on Amazon UK »Full Review:
In an emergency, having the right first aid supplies at home can prevent minor injuries from becoming major issues. This Rennington first aid kit meets BS8599-1 standards — the gold standard in the UK for first aid contents.
It includes over 90 essential items:
- Assorted sterile dressings
- Burn relief gel
- Triangular bandages
- Adhesive plasters
- Eye wash pods
- Nitrile gloves
- Shears and safety pins
The case is hard, waterproof, and wall-mountable — ideal for home kitchens, workshops, or home offices. The internal compartments are labelled for fast, stress-free access during an emergency.
This isn’t just a collection of plasters. It’s a complete, standards-compliant emergency kit used by professionals and businesses — and it’s just as important in your home.
Pros:
- BS8599-1 compliant for homes and offices
- Excellent range of high-quality components
- Sturdy and waterproof case
- Suitable for families, landlords, and remote workers
Cons:
- Contents have expiry dates — periodic checks needed
- Not pocket-sized (but perfect for storage cabinets)
Best for: Households that want to be truly prepared for injuries, burns, or minor emergencies.
🛁 5. KEPLIN Premium Non-Slip Bath Mat

💰 Price: Approx. £6.99
⭐ Rating: 4.7/5
📦 Buy on Amazon UK »Full Review:
Slipping in the bath or shower isn’t just a minor incident — it’s one of the leading causes of injury at home, especially for older adults. This KEPLIN bath mat is an inexpensive yet effective fix.
Made with anti-microbial PVC and hundreds of suction cups, it stays firmly in place even on slippery tubs. Its textured surface helps your feet grip securely, and drainage holes prevent water from pooling beneath.
It’s also mould-resistant and machine washable, making maintenance simple. For under £10, this is a no-brainer for anyone who wants to make their bathroom safer.
Pros:
- Strong grip and textured anti-slip surface
- Mould and mildew-resistant
- Generously sized and machine washable
- Excellent price point
Cons:
- Needs regular cleaning to stay fresh
- May not stick well to textured tubs
Best for: Bathrooms shared with children, elderly residents, or anyone with balance/mobility challenges.
✅ Final Thoughts
These five products cover the most important safety risks in UK homes:
- Fire hazards 🔥
- Carbon monoxide poisoning 💨
- Child access 🚼
- Minor injuries 🚑
- Slip-and-fall accidents 🛁
Each item is:
- ✅ Highly rated and reviewed
- ✅ Easy to install or use
- ✅ Extremely cost-effective
Even implementing just one or two of these safety upgrades could protect your loved ones and prevent life-changing accidents.
-

Lessons from the Grenfell Tower Fire: A Comprehensive Analysis
On 14 June 2017, a kitchen fire in Flat 16 of Grenfell Tower—a 24‑storey residential block in North Kensington, London—escalated into one of the deadliest modern high‑rise conflagrations. By the time the blaze was extinguished, 72 people had perished and dozens more were injured or displaced—exposing a cascade of preventable safety failures: from combustible cladding and flawed evacuation policies to fractured regulatory oversight. In this post, we unpack the critical breakdowns, trace the ensuing inquiry and reforms, and lay out actionable lessons for facility managers, EHS professionals, landlords, and homeowners alike.
1. Rapid Fire Spread: The Cladding Catastrophe
1.1 Combustible ACM Panels
- Aluminium Composite Material (ACM): The tower’s 2015–16 recladding used ACM panels with a polyethylene core, a highly flammable plastic that fed the vertical “chimney effect,” carrying flames up the façade in under 20 minutes .
- Burning Dynamics: When ignited, molten droplets from the polyethylene core fell to lower floors, igniting debris and accelerating the spread .
1.2 Misleading Certifications & Cost‑Cutting
- Regulatory Loopholes: Manufacturers and installers exploited gaps in fire‑performance testing requirements, submitting outdated data to secure planning approval .
- Value Engineering: The original specification called for non‑combustible insulation, but a switch to cheaper polyethylene‑cored panels went unchallenged by building control .
2. Evacuation Policy Breakdown
2.1 “Stay Put” Doctrine
- Standard Practice: UK high‑rise regulations prescribe that residents remain in their flats during fires to leverage compartmentation.
- Fatal Misapplication: Once flames breached multiple flats via the cladding, the “stay put” instruction trapped occupants in deadly smoke and heat .
2.2 Conflicting Instructions & Panic
- Mixed Messages: As conditions worsened, some residents were first told to stay put, then abruptly ordered to evacuate—leading to confusion in smoke‑filled stairwells.
- Lack of Real‑World Drills: No evacuation scenario had anticipated a rapid external façade failure; residents and staff were unprepared for a full‑building exit in minutes.
3. Regulatory & Oversight Failings
3.1 Fragmented Responsibility
- Multiple Stakeholders: The council, building-control inspectors, architects, contractors, and fire authorities each assumed safety was “someone else’s” duty .
- Paper‑Driven Inspections: Audits focused on documents over practical tests—there was no requirement to verify the as‑installed cladding against certified samples .
3.2 Weak Enforcement & Whistle‑blowing Gaps
- Lenient Penalties: Non-compliance often resulted in slow or absent follow‑up, emboldening cost‑cutting and design shortcuts.
- Silenced Concerns: Workers and residents who flagged safety issues were sidelined or ignored, perpetuating a culture of complacency.
4. The Public Inquiry & Legislative Reforms
4.1 Inquiry Phases & Key Findings
- Phase 1 (March 2020): Detailed the events of the night, highlighting alarm failures and emergency‑service challenges .
- Phase 2 (September 2024): Delivered 58 recommendations, including a full ban on combustible cladding, mandatory resident engagement, and streamlined regulatory oversight .
4.2 Building Safety Act 2022
- New Regulator: The Building Safety Regulator, housed within the Health & Safety Executive, now oversees “high‑risk” buildings (≥18 m) .
- Golden Thread of Information: Mandates a continuous, digital record of design, construction, and maintenance data accessible to residents and authorities .
- Stricter Fire‑Safety Certification: Non‑compliant buildings must produce valid safety certificates before occupation or face enforcement action.
5. Long‑Term Impacts & Community Rebuilding
- Survivor Health: Many evacuees and first responders suffer chronic respiratory, psychological, and cardiovascular issues due to prolonged smoke exposure and trauma .
- Environmental Cleanup: Soil and water around the site remain contaminated by debris and toxic residues, requiring multi‑year remediation.
- Resident Empowerment: Survivor advocacy led to resident‑led safety committees, ensuring community voices drive ongoing safety audits and reforms.
6. Actionable Lessons for EHS Professionals, Companies & Homeowners
- Independent Material Vetting
- Always commission third‑party fire‑performance tests for cladding and insulation—never rely solely on manufacturer certifications.
- Redundancy & Fail‑Safe Design
- Build multiple, independent layers of protection (e.g., sprinklers, pressurised escape routes, external monitors) so no single failure triggers disaster.
- Comprehensive Evacuation Planning
- Conduct multi‑scenario drills (compartment breaches, full‑building evacuations) and update policies after any retrofit or design change.
- End‑to‑End Accountability
- Create a transparent “responsibility matrix” mapping every stakeholder’s duties, with formal sign‑offs at each project stage.
- Resident & Worker Engagement
- Establish protected channels for safety concerns—regular town halls, feedback surveys, and whistle‑blower policies.
7. Enforcement, Fines & Prosecutions: The High Cost of Complacency
In the wake of Grenfell, regulators have signaled zero tolerance for fire‑safety lapses—issuing severe penalties to both organisations and individuals:
- Corporate Fines & Prosecutions:
Under the Regulatory Reform (Fire Safety) Order 2005, businesses face unlimited fines, and directors can be prosecuted for gross negligence. Housing associations and councils have been fined over £100,000 per offence for invalid or missing fire‑risk assessments. - Individual Liability:
Landlords and homeowners are not exempt. Private landlords have received £20,000+ fines and community sentences for installing non‑compliant doors or neglecting smoke‑alarm maintenance—sometimes facing prosecution for endangering occupants.
How It Could Have Been Avoided
A proactive EHS programme—combining independent material testing, regular fire‑risk assessments, and both “stay‑put” and full‑evacuation drills—prevents small oversights from cascading into catastrophe. Clear accountability, documented sign‑offs at every stage, and empowered whistle‑blower channels ensure safety concerns surface well before regulatory intervention.
8. Fire‑Safety Support & Compliance Resources
Whether you oversee a high‑rise block, manage a business premises, or simply want to protect your home, we can help you:
- Downloadable Fire‑Risk Assessment Templates for both commercial and residential properties.
- Golden Thread Compliance Systems, logging every design change, inspection, and drill in a secure digital platform.
- Staff & Resident Training Programs covering multi‑scenario evacuation planning and proper use of firefighting equipment.
- Quarterly Compliance Audits & Legislative Updates to keep you ahead of evolving fire‑safety regulations.
🛡️ Homeowner Tip:
Install and test smoke and CO alarms on every floor monthly. Replace batteries yearly and keep a simple log of your checks—this small practice can be the difference between an early alert and a legal prosecution.
By integrating these Grenfell Tower fire safety lessons—from rigorous material vetting and evacuation planning to robust accountability and community engagement—you safeguard lives and protect against devastating financial and legal repercussions. Get in touch today for tailored fire‑safety resources and compliance support, and let’s build a safer future together.
-

Incident Reporting: Legal Essentials and Top Investigation Methods
Effective incident reporting methods are the backbone of a proactive safety management system. Not only do they help you comply with legal obligations, but they also enable you to learn from incidents, prevent reoccurrences, and foster a culture of continuous improvement. In this expanded guide, you’ll find:
- An Introduction to Incident Reporting
- Legal Requirements and Your Duties
- Detailed Walkthrough of the 5 Whys Analysis
- Step‑by‑Step Fishbone (Ishikawa) Diagram Method
- In‑Depth Guide to Fault Tree Analysis (FTA)
- Choosing the Right Method for Your Organisation
- Tips for Embedding Robust Reporting Processes
- Conclusion & Next Steps
- Focus Keyword, Tags, and Meta Description
Ready to streamline your incident reporting? Each methodology section ends with an invitation to request a free template or engage our full-service support. Let’s dive in.
1. Introduction to Incident Reporting
Incident reporting captures details of workplace events—ranging from near misses to serious injuries—and translates them into actionable insights. Without consistent reporting:
- Hazards remain hidden until they cause harm.
- Root causes go unidentified, leading to repeat occurrences.
- Legal non-compliance risks fines, enforcement notices, or prosecution.
By mastering proven incident reporting methods, you’ll empower teams to identify risks early, implement corrective measures, and demonstrate to stakeholders that safety is a top priority.
2. Legal Requirements and Your Duties
In the UK, specific regulations mandate when and how incidents must be reported:
RIDDOR 2013 (Reporting of Injuries, Diseases and Dangerous Occurrences Regulations)
- Reportable Incidents: Fatalities; specified injuries (e.g., fractures, amputations); over-seven-day injuries; occupational diseases; and dangerous occurrences (near misses with high potential).
- Timeframes: Fatalities and major injuries must be reported within 10 days; dangerous occurrences within 15 days; diseases and over-seven-day injuries can be reported online as soon as practicable.
- Duty Holders: Employers, people in control of premises, and self-employed individuals in certain industries.
Health and Safety at Work etc. Act 1974
- General Duty: Employers must ensure, so far as is reasonably practicable, the health, safety and welfare of employees.
- Record‑Keeping: Maintain records of incidents and investigations as evidence of due diligence.
Management of Health and Safety at Work Regulations 1999
- Risk Assessments: Requires employers to carry out “suitable and sufficient” assessments and take preventative or protective measures.
Failing to follow these requirements can result in heavy penalties, reputational damage, and, in severe cases, custodial sentences for directors. A documented incident reporting process not only ensures compliance but also underpins continuous safety improvements.
3. Detailed Walkthrough of the 5 Whys Analysis
The 5 Whys technique is a straightforward yet powerful root cause analysis tool. By repeatedly asking “why?”, teams dig beneath surface symptoms to reveal the underlying issue.
Why Choose 5 Whys?
- Simplicity: No special training or software required.
- Speed: Typically completed in a single meeting or toolbox talk.
- Focus: Encourages collaborative problem‑solving and ownership of solutions.
Step‑by‑Step Guide
- Gather the Team: Include individuals familiar with the incident, such as operators, supervisors and safety officers.
- Define the Problem: Write a clear, concise description of the incident at the top of your worksheet.
- Ask Why #1: Why did the incident happen? Record the answer verbatim.
- Continue Asking Why: Repeat until you reach a root cause—often before the fifth why.
- Validate the Cause: Verify through data, observations or testing that your identified cause is accurate.
- Develop Corrective Actions: Target solutions at eliminating or mitigating the root cause.
Example Scenario
- Incident: A warehouse worker trips over an electrical cable.
- Why 1? Because the cable was across the walkway.
- Why 2? Because there was no cable management system installed.
- Why 3? Because the standard operating procedure (SOP) didn’t mandate cable clips.
- Why 4? Because the incident report template lacked a section for housekeeping controls.
- Why 5? Because the original template was designed without input from maintenance staff.
Outcome & Action: Update your incident reporting and assessment templates to include housekeeping checks and cable management before tasks begin.
Need a free 5 Whys template or full-service support? Contact us.
4. Step‑by‑Step Fishbone (Ishikawa) Diagram Method
The Fishbone Diagram (or Ishikawa) offers a visual framework to explore all potential causes of an incident.
Benefits of Fishbone Diagrams
- Holistic View: Categorises causes for comprehensive analysis.
- Team Collaboration: Encourages brainstorming from multiple perspectives.
- Clarity: Makes complex interactions easy to visualise.
Creating Your Fishbone Diagram
- Draw the Backbone and Head: At the right end, write the incident description.
- Select Major Categories: Typical headings include People, Process, Equipment, Materials, Environment, and Management.
- Brainstorm Sub‑Causes: Under each category, list factors that may have contributed.
- Review & Validate: Vote or use data to prioritise the most likely causes.
- Action Planning: Assign mitigation measures for each high‑priority cause.
Example Breakdown
- People: Inadequate training on new equipment.
- Process: No checklist for shift handovers.
- Equipment: Outdated guard on conveyor belt.
- Materials: Packaging debris accumulating near machinery.
- Environment: Poor lighting in the loading bay.
- Management: No regular housekeeping audits scheduled.
Armed with this diagram, your team can tackle each root category systematically.
Looking for a free Fishbone Diagram template or expert facilitation? Contact us.
5. In‑Depth Guide to Fault Tree Analysis (FTA)
Fault Tree Analysis is a rigorous, logic-based method ideal for complex systems where multiple failures can converge.
Why Use FTA?
- Precision: Models how combinations of faults lead to an incident.
- Quantification: Enables probability estimation when data is available.
- Complex Systems: Suited for manufacturing lines, process plants, and safety-critical operations.
Building Your Fault Tree
- Define the Top Event: Place the incident outcome (e.g., system shutdown) at the top.
- Identify Immediate Causes: Link them with OR gates if any cause alone triggers the event, or AND gates if multiple must occur together.
- Decompose Further: Break each cause down into more granular sub-events.
- Assign Probabilities (Optional): For each basic event, use historical data or expert judgment.
- Analyze and Mitigate: Locate minimal cut sets—combinations of failures that cause the top event—and implement controls.
Simplified Example
- Top Event: Conveyor belt malfunction causing downtime.
- Branch 1 (Motor Overload): Motor overheating OR voltage spike.
- Branch 2 (Belt Misalignment): Worn rollers AND lack of maintenance.
- Branch 3 (Control Failure): Faulty sensor OR software glitch.
By targeting the minimal cut sets—such as implementing thermal overload protection and a predictive maintenance schedule—you can prevent the top event.
Want a free Fault Tree Analysis template or full-service FTA facilitation? Contact us.
6. Choosing the Right Method for Your Organisation
No single method fits all contexts. Consider:
- Complexity: Use FTA for multi-component systems; opt for 5 Whys on straightforward events.
- Team Size & Expertise: Fishbone works well in group workshops; 5 Whys can be done quickly by small teams.
- Data Availability: If you have rich historical data, FTA’s probabilistic approach adds value.
Often, combining methods—starting with 5 Whys, expanding with a Fishbone, then validating critical paths in FTA—yields the most robust insights.
7. Tips for Embedding Robust Reporting Processes
- Simplify Your Forms: Ensure required fields are clear and intuitive.
- Train Regularly: Conduct annual workshops and toolbox talks on reporting procedures.
- Leverage Technology: Adopt mobile apps for real-time submissions and analytics.
- Close the Loop: Share outcomes of investigations with all staff to reinforce trust.
- Set Clear SLAs: Define timelines for initial report review, investigation completion and action closure.
Embedding these practices ensures your incident reporting remains effective, compliant and continuously improving.
8. Conclusion & Next Steps
Mastering incident reporting methods equips your organisation to meet legal requirements under RIDDOR, HSW Act and Management Regulations while harnessing incidents as opportunities for improvement. Whether you choose 5 Whys, Fishbone Diagrams or Fault Tree Analysis, the key is consistent application and follow‑through on corrective actions.
Ready to elevate your incident reporting?
- Free Templates: Request an editable 5 Whys, Fishbone and FTA template tailored to your needs.
- Full-Service Support: Engage our expert consultants to facilitate workshops, customise forms and integrate digital solutions.
Visit our Contact Us page now to get started—no cost, no obligation.
-
Free H&S Risk Assessment Template: How to Use It for Workplace Safety
Ensuring a safe working environment isn’t just about ticking boxes—it’s about protecting your team, your reputation, and your bottom line. A well-structured H&S risk assessment template is the cornerstone of any proactive health and safety (H&S) programme. In this comprehensive guide, you’ll discover:
- Why a Risk Assessment Matters
- Key Legislative Requirements & Standards
- Anatomy of an H&S Risk Assessment Template
- Step-by-Step Instructions for Completion
- Using a Risk Matrix to Prioritise Hazards
- Implementing and Monitoring Control Measures
- Case Study: Real-World Application
- Common Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
- Digital Tools & Automation for Streamlined Assessments
- Embedding Safety Culture Across Your Organisation
- Measuring Success & Continuous Improvement
- Next Steps & How to Request Your Free Template
And if you’d like an editable, bespoke template you can adapt to your specific operations, simply contact us to request your free H&S risk assessment template today!
1. Why a Risk Assessment Matters
A risk assessment template is more than compliance paperwork—it’s your roadmap to:
- Protecting People: By identifying hazards such as slips, trips, machinery entanglement or chemical exposure, you can act before injuries occur.
- Reducing Costs: Preventing accidents saves on lost production, insurance premiums and legal fees.
- Ensuring Compliance: UK law mandates employers assess and control risks; a documented assessment demonstrates due diligence.
- Driving Continuous Improvement: Regular reviews encourage refinement of procedures, training and resource allocation.
2. Key Legislative Requirements & Standards
A robust H&S programme aligns with these critical frameworks:
- Health and Safety at Work etc. Act 1974: Primary UK legislation placing a duty on employers to safeguard employees’ health and safety.
- Management of Health and Safety at Work Regulations 1999: Requires suitable and sufficient risk assessments covering hazard identification, risk evaluation and control implementation.
- ISO 45001:2018: Global standard for Occupational Health & Safety Management Systems, promoting legal compliance and performance improvement.
- COSHH Regulations 2002: Governs the management of hazardous substances, including specific risk assessments for chemical exposure.
3. Anatomy of an H&S Risk Assessment Template
Every effective template guides you through these essential sections:
- Activity Description: Define the scope, for example “Forklift loading operation in warehouse Bay 3.”
- Hazard Identification: List specific hazards, such as unguarded moving parts or manual handling risks.
- Who Might Be Harmed: Identify affected groups—operators, maintenance staff, visitors.
- Risk Evaluation: Rate likelihood and severity on a simple 1–5 scale.
- Risk Score: Multiply likelihood by severity to prioritise hazards.
- Control Measures: Document existing controls (Guards, PPE, training) and propose additional measures.
- Priority & Action Owner: Assign each action a priority level, responsible person and deadline.
- Review Date: Schedule the next reassessment—at least annually or after any significant change.
- Notes & Comments: Capture observations, worker suggestions or follow-up items.
4. Step-by-Step Instructions for Completion
- Select and Describe the Activity
- Focus on highest-risk tasks such as machinery operation or chemical handling.
- Provide enough detail so reviewers understand the exact process.
- Walk the Process and Engage Staff
- Conduct a physical walkthrough.
- Interview front-line staff to uncover hidden hazards.
- Identify Hazards Precisely
- Replace generic terms with specifics (e.g., “unguarded rotating shafts on Press A”).
- Consider environmental factors like noise or temperature extremes.
- Evaluate Risk
- Assign a likelihood score (1 = Rare to 5 = Almost Certain).
- Assign a severity score (1 = Minor injury to 5 = Fatality).
- Calculate the Risk Score
- Multiply likelihood by severity to get a numerical score.
- Use colour codes or tiers (e.g., 1–6 = Low, 7–12 = Medium, 13–25 = High).
- Document Controls
- List existing measures first (e.g., guards, PPE).
- Propose new controls: engineering fixes, administrative updates, or training.
- Assign Actions and Deadlines
- Set realistic timeframes and responsibility, such as:
- Action: Install pressure-sensitive mat on press base
- Owner: Jamie Lee
- Deadline: 15 Aug 2025
- Set realistic timeframes and responsibility, such as:
- Review and Close Out
- Confirm actions are completed, update the template and reset the review cycle.
- Record evidence of completion, like photos or emails.
5. Using a Risk Matrix to Prioritise Hazards
A visual risk matrix enables quick identification of high-risk areas. For example, a simple 5×5 grid where:
- The vertical axis represents Likelihood (1–5)
- The horizontal axis represents Severity (1–5)
- Each cell is colour-coded: Green for Low, Amber for Medium, Red for High
Embed this matrix in your template or digital tool to auto-highlight critical items.
6. Implementing and Monitoring Control Measures
- Engineering Controls: Machine guards, interlocks, ventilation systems.
- Administrative Controls: Updated procedures, safety signage, shift rotations.
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Last line of defence—ensure fit, selection and training.
- Monitoring: Schedule monthly inspections, maintain a near-miss reporting system and hold regular review meetings with action owners.
Document all findings and follow up until each control is verified as effective.
7. Case Study: Real-World Application
Scenario: A manufacturing company faced frequent near misses at a stamping press.
Steps Taken:
- Identified unguarded moving parts and poor housekeeping.
- Rated risk as High (Likelihood 4 × Severity 4 = 16).
- Proposed controls: install fixed guards, implement floor-marking zones and weekly housekeeping checks.
- Assigned actions with deadlines and owners.
Outcome: Zero near misses over three months, an 8% reduction in insurance premiums and positive audit feedback from HSE inspectors.
8. Common Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
- Vague Hazard Entries: Always use precise descriptions (e.g., “oil spill near Packing Bay 2”).
- Skipping Worker Engagement: Conduct short workshops or toolbox talks before completing the form.
- One-Time Assessments: Schedule reassessments at least annually and after any incident.
- Over-Engineering Controls: Balance cost versus benefit—sometimes signage or training suffices.
- Lack of Follow-Up: Use digital reminders or calendar alerts to track and close out actions.
9. Digital Tools & Automation for Streamlined Assessments
- Mobile Inspection Apps: Capture data, photos and trigger reminders on the go.
- Cloud-Hosted Risk Registers: Centralise assessments, track trends and generate dashboards.
- Automated Reminders: Emails triggered when review dates or deadlines approach.
- Analytics & Reporting: Quickly identify top hazards, overdue actions and training gaps.
Ask us about integrating these tools when you contact us.
10. Embedding Safety Culture Across Your Organisation
- Leadership Involvement: Have senior management review high-risk items quarterly.
- Continuous Communication: Share lessons learned in newsletters and meetings.
- Recognition Programs: Reward teams for proactive hazard reporting and action-closure rates.
- Training & Development: Refresh assessors on best practices and emerging risks, such as ergonomic hazards or remote-work stress.
11. Measuring Success & Continuous Improvement
Track these key performance indicators (KPIs):
- Number of assessments completed
- Actions closed versus overdue
- Incident and near-miss trends
- Audit findings and compliance scores
- Employee safety perception survey results
Review these metrics quarterly to ensure your H&S programme evolves effectively.
12. Next Steps & How to Request Your Free Template
A tailored, editable H&S risk assessment template simplifies the start of your safety programme. To request yours:
- Visit our Contact Us page.
- Tell us about your organisation and primary activities.
- Receive your bespoke, fully editable template within one business day—no cost, no obligation.
Start your journey to a safer workplace today. Complete your first assessment, close out actions, and watch your incident rates—and costs—fall.
-

Mastering HSE Interview Questions: Top 5 Scenarios & STAR Answers
Landing your first or next HSE role often hinges on how well you handle HSE interview questions. Interviewers want to see not only your technical knowledge but also your problem‑solving, communication, and leadership skills under pressure. The STAR method (Situation, Task, Action, Result) is the gold standard for structuring concise, impactful answers. In this SEO‑optimized guide, we cover the five most common HSE interview scenarios, provide sample STAR answers, and show you how to tailor your responses for each HSE interview questions to stand out.
1. Risk Assessment Challenge
Question: “Tell us about a time you identified a significant risk on site. What did you do?”
-
Situation: During my placement with XYZ Construction, I noticed workers stacking heavy pallets near a pedestrian walkway, creating a crush hazard.
-
Task: As the junior HSE assistant, I needed to halt unsafe practices and implement a safer procedure.
-
Action: I paused operations, conducted a quick toolbox talk explaining the risk, and collaborated with the site supervisor to redesign the storage zone away from foot traffic. I then updated the site’s risk register and added new control measures, including directional signage and routine storage audits.
-
Result: Within a week, there were zero near‑miss reports in that area, and the control measures were adopted across two other sites, reducing overall material‑handling incidents by 30 %.
Why It Works: Demonstrates proactive hazard recognition, communication skills, and measurable impact.
2. Incident Investigation Scenario
Question: “Describe when you led or assisted in an incident investigation.”
-
Situation: At my internship with ABC Manufacturing, a slip‑and‑fall incident led to a fractured wrist for an operator.
-
Task: I was tasked with gathering facts, identifying root causes, and proposing corrective actions.
-
Action: I secured the scene, took photographs, interviewed witnesses, and reviewed CCTV. Using a Fishbone Diagram, I traced the cause to a leaking coolant pipe and inadequate spill‑response training. I worked with maintenance to repair the pipe and developed a new spill‑response SOP, delivering refresher training to all shift teams.
-
Result: No repeat incidents occurred in six months, and production downtime due to spills decreased by 45 %.
Why It Works: Highlights methodical investigation, use of analytical tools, and effective follow‑through.
3. Compliance Audit Preparation
Question: “Give an example of how you prepared for an internal or external HSE audit.”
-
Situation: My previous employer faced an ISO 45001 surveillance audit with the registrar scheduled in two weeks.
-
Task: As part of the audit team, I had to ensure documentation and site practices were audit‑ready.
-
Action: I conducted a gap analysis against the ISO 45001 checklist, updated missing entries (e.g., training records, risk‑assessment revisions), and led a mock audit—rotating auditors to simulate fresh eyes. I also briefed department heads on interview techniques and organized a pre‑audit walkthrough with senior management.
-
Result: The registrar issued zero major non‑conformities and only two minor observations, both closed within 10 days.
Why It Works: Demonstrates planning, documentation control, and stakeholder engagement.
4. Emergency Response Leadership
Question: “Share a time you coordinated an emergency drill or real response.”
-
Situation: During my time at DEF Logistics, we needed to test our chemical‑spill response plan for a newly installed bund area.
-
Task: I was appointed “Incident Controller” for the drill, responsible for scenario design and team coordination.
-
Action: I drafted a realistic script involving a simulated leak, assigned roles to spill‑team members, and integrated first responders. Post‑drill, I facilitated a debrief to capture lessons learned and revised the ERP to include clearer communication protocols and updated PPE requirements.
-
Result: The next unannounced drill saw a 40 % faster containment time and positive feedback from our corporate safety auditor.
Why It Works: Shows leadership under pressure, planning skills, and iterative improvement.
5. Stakeholder Engagement & Influence
Question: “How have you influenced non‑HSE staff to follow safety procedures?”
-
Situation: At my university HSE society, I noticed low attendance at monthly safety talks among lab technicians.
-
Task: I needed to boost engagement and practical uptake of lab safety practices.
-
Action: I revamped the format—introducing hands‑on demos (e.g., correct eyewash use) and short “mini‑quizzes” with prizes. I also collaborated with lab managers to incorporate the talks into mandatory training schedules and sent friendly reminder emails highlighting real lab‑incident case studies.
-
Result: Attendance jumped from 20 % to 80 %, and post‑session surveys showed a 95 % increase in reported confidence handling lab hazards.
Why It Works: Illustrates creativity, collaboration, and measurable behaviour change.
Preparing Your Own STAR Answers
-
Brainstorm Scenarios: List 8–10 experiences from internships, projects, or volunteering.
-
Structure Each with STAR: Keep answers to 1–2 minutes.
-
Quantify Results: Use percentages, time saved, or incident reductions.
-
Rehearse Aloud: Practice with a peer or record yourself to refine clarity and confidence.
Ready to Ace Your HSE Interview?
Don’t leave your career to chance. Contact us to book a mock interview—complete with personalized feedback on your HSE interview questions and STAR answers, body language coaching, and sector‑specific question banks. We’ll help you enter your next HSE interview with poise and professionalism.
-
-

Navigating the Global HSE Job Market: Entry‑Level Opportunities & Salary Benchmarks
Breaking into Health, Safety & Environment (HSE) can feel daunting, but demand for junior HSE professionals is growing worldwide. From major infrastructure projects in North America to manufacturing hubs in Asia and energy centres in the Middle East, entry‑level opportunities abound. In this SEO‑optimized guide, we’ll outline the most common early‑career HSE roles across regions, provide international salary benchmarks, and share where to find your ideal first position—plus how to sign up for our free global HSE job‑alert list and get a complimentary CV review.
1. The Global HSE Job Landscape in 2025
-
North America: Strong demand in oil & gas (Texas, Alberta), construction (U.S. infrastructure bills), and tech campuses (California).
-
Europe: Growth in renewable energy (Germany, Nordics), manufacturing (Poland, Czech Republic), and logistics (Netherlands).
-
Asia & Pacific: Rapid urbanisation fuels roles in Singapore, Hong Kong, Australia, and expanding industrial parks across Southeast Asia.
-
Middle East & Africa: Large‑scale projects in the UAE, Saudi Arabia, and South Africa create entry‑level openings in construction, petrochemicals, and utilities.
Across all regions, organisations seek NEBOSH or ISO 45001‑aligned competence, foundational risk‑assessment skills, and familiarity with digital audit and incident‑management tools.
2. Common Entry‑Level HSE Roles & Core Responsibilities
While titles vary, here are five roles you’ll encounter globally:
-
HSE Coordinator / Assistant
-
Update risk registers and assist in site audits
-
Track training compliance and incident reports
-
Employed in consultancies, contractors, and corporate HSE teams
-
-
Junior Safety Advisor
-
Conduct regular safety inspections, report findings
-
Deliver toolbox talks and safety briefings
-
Found in construction sites, manufacturing plants, and large campuses
-
-
Environmental Compliance Technician
-
Monitor emissions and effluents, support permit compliance
-
Perform sampling and basic laboratory work
-
Common in utilities, waste‑management, and mining sectors
-
-
Quality, Health & Safety Officer
-
Aid ISO 9001 and ISO 45001 certification processes
-
Maintain documentation control and CAPA tracking
-
Popular in food & beverage, pharmaceuticals, and automotive
-
-
Graduate HSE Trainee
-
Rotate through departments to learn FRA and contractor management
-
Support policy reviews, data entry, and management reporting
-
Offered by global corporations via structured graduate schemes
-
Pro Tip: Early‑career roles often blend health, safety, and environmental duties. Embrace that diversity to accelerate your learning curve.
3. International Salary Benchmarks
While compensation varies by country, here are approximate entry‑level ranges in 2025:
-
United States & Canada: US $45,000 – $60,000 / CAD $50,000 – $65,000
-
United Kingdom & Ireland: £24,000 – £30,000 / €30,000 – €36,000
-
Western Europe: €30,000 – €38,000 (Germany, Netherlands, Nordics)
-
Asia & Pacific: SGD 40,000 – SGD 55,000 (Singapore); AUD 60,000 – AUD 75,000 (Australia)
-
Middle East: AED 80,000 – AED 100,000 / SAR 75,000 – SAR 95,000
-
Africa: ZAR 200,000 – ZAR 280,000 (South Africa); USD 20,000 – USD 30,000 (emerging markets)
Insight: Always factor in regional cost‑of‑living, expatriate allowances, and tax treatments when evaluating offers.
4. Top Channels to Find Global Entry‑Level HSE Jobs
-
Global Job Boards:
-
LinkedIn (filter by “Entry level” and region)
-
Indeed Worldwide, Glassdoor
-
-
Specialist Safety Portals:
-
OSHCR (UK), SafetyJobs (Europe), HSE‑Jobs (Middle East)
-
-
Professional Bodies & Training Providers:
-
NEBOSH’s Career Centre, IOSH’s Global Jobs Portal
-
Local OSHA equivalents and national safety councils
-
-
Graduate & Internship Programmes:
-
Corporate schemes at BP, Shell, Siemens, Tata Group
-
University career services and global internship fairs
-
-
Networking & Social Media:
-
Join HSE communities on LinkedIn, Facebook groups (e.g., “Global HSE Professionals”)
-
Attend virtual conferences (Safety & Health Expo, ASSE Safety Conference)
-
Pro Tip: Set up real‑time alerts on LinkedIn and Indeed for your focus keyword—global entry‑level HSE roles—to stay first in line.
5. Standing Out in a Crowded Market
-
SEO Your CV & Online Profile: Use your focus keyword in your headline and summary.
-
Highlight Quantifiable Achievements: Detail project contributions, audit support, or safety campaigns you led in academia or internships.
-
Tailor Applications by Region: Emphasise local regulations (e.g., OSHA in the U.S., EU OSHA directives, Singapore’s WSH Act) to show readiness.
-
Digital Portfolio & Thought Leadership: Post safety‑related articles, case studies, or process-improvement write‑ups on LinkedIn.
Free Resource: Contact us to receive our “Global HSE CV & LinkedIn Template Pack” and secure a complimentary CV review from a regional HSE expert.
6. Next Steps & Career Development
-
Certifications: Plan to complete NEBOSH International General Certificate or ISO 45001 Lead Implementer within 12 months.
-
Continuous Professional Development (CPD): Log training and practical experiences—seek CPD schemes offered by IOSH, ASSE, or local bodies.
-
Mentoring & Networking: Engage in cross‑border mentor programmes (e.g., IOSH Mentoring Hub) and local HSE chapters to expand your global perspective.
Stay Connected: Sign up for our free global HSE job‑alert list—receive curated entry‑level openings from all major regions directly to your inbox. Sign up here!
Embarking on your HSE career internationally is an exciting opportunity. With the right market insights, targeted applications, and ongoing support, you’ll secure your first role and fast‑track your path to global HSE leadership.
Ready to launch your global HSE career?
📞 Contact us today for your free CV review, job‑alert subscription, and personalised career coaching! -
-

Implementing ISO 45001 in UAE Free Zones : Step‑by‑Step Best Practices
Navigating the complexities of occupational health and safety (OH&S) in UAE Free Zones demands a structured, risk-based approach that aligns global standards with local regulations. Whether you operate in Jebel Ali Free Zone (JAFZA), Dubai Multi Commodities Centre (DMCC), or Ras Al Khaimah Economic Zone (RAKEZ), ISO 45001 certification not only enhances workplace safety but also reinforces your credibility in highly competitive sectors like oil & gas, logistics, manufacturing, and trade.
In this comprehensive guide, we delve into every phase of ISO 45001 implementation—from initial gap analysis to certification audits—adding region-specific insights, multilingual strategies, and practical tools to streamline your OH&S journey. By embedding these best practices, you’ll reduce incidents, lower insurance premiums, and unlock new business opportunities across the Middle East and beyond.
Throughout the article, you’ll find detailed checklists, real-world examples, and downloadable templates designed for UAE Free Zone environments. We also highlight how partnering with an experienced OH&S consultancy can accelerate your timeline and ensure compliance with local directives.
Ready to elevate your safety management system? Read on for a step-by-step roadmap that transforms ISO 45001 from a regulatory checkbox into a competitive advantage. If you need tailored support at any stage, contact us for expert guidance, tools, and services.
Why ISO 45001 Matters in UAE Free Zones
- Regulatory Alignment: UAE Free Zones (e.g., JAFZA, DMCC, DAFZA, RAKEZ) enforce stringent OH&S frameworks to maintain operator licenses. ISO 45001 bridges global best practices with these local mandates, mitigating the risk of fines, shutdowns, or reputational damage.
- Systematic Risk Reduction: With ISO 45001’s structured risk assessment process, you can proactively identify hazards—from hot work to chemical handling—and implement targeted controls, significantly reducing incident rates and operational downtime.
- Competitive Differentiator: Certification demonstrates commitment to employee welfare and risk management, making your company a preferred partner for international clients, investors, and regulatory bodies.
🛠️ Step‑by‑Step Implementation Roadmap
1. Conduct an Initial Gap Analysis
- Legal & Regulatory Review
- Applicable Laws: List UAE-wide statutes (e.g., Federal Decree-Law No. 33/2021) and Free Zone regulations (e.g., JAFZA Safety Regulations, DMCC Compliance Manual).
- Clause Mapping Matrix: Align each ISO 45001 clause with relevant local directives to pinpoint compliance gaps.
- Current State Assessment
- Process Inventory: Catalog existing OH&S elements—incident logs, training records, equipment inspections, PTW forms.
- Gap Identification & Prioritization: Assign risk scores and compliance levels to missing or partial processes, focusing on those with highest safety impact.
Pro Tip: Accelerate analysis with our pre-configured Gap Analysis Template.
Contact us for free access and expert review.2. Secure Leadership Commitment
- Executive Briefing
- Present incident trends, risk-cost analysis, and case studies showing ROI of ISO 45001 certification.
- Facilitate a workshop to finalize your OH&S Policy, ensuring it reflects Free Zone-specific requirements and corporate values.
- Roles & Responsibilities
- Project Champion: Senior HSE or QHSE Manager to oversee implementation.
- Functional Owners: Define clear accountability for hazard identification, incident response, training, and audit activities.
3. Develop Your OH&S Management System (OHSMS)
3.1 Planning
- Risk & Opportunity Register
- Conduct cross-functional hazard identification sessions.
- Use a 1–5 likelihood-severity risk matrix to quantify each hazard.
- Document improvement opportunities (automation, ergonomic tools) alongside risks.
- Objectives & KPIs
- Set SMART goals (e.g., “Reduce lost-time injuries by 25% by Q1 2026”).
- Track leading indicators (training completion) and lagging indicators (incident frequency rate) via a dynamic dashboard.
Need tailored e‑learning content?
Contact us to develop multilingual, interactive training modules.3.2 Support
- Competence & Training
- Perform a Training Needs Analysis for all roles.
- Develop materials in English, Arabic, Hindi/Urdu; include visual aids for high-impact retention.
- Monitor completion and assessment results in an LMS or compliance tracker.
- Communication Protocols
- Establish multi-channel updates: email alerts, WhatsApp groups, digital signage.
- Schedule regular toolbox talks and quarterly safety forums with multilingual translation.
4. Operational Control & Documentation
- Process Mapping & Document Control
- Create detailed flowcharts for high-risk tasks (confined space, hot work).
- Implement a document control system with versioning and approval workflows.
- Permit‑to‑Work (PTW) System
- Evaluate digital PTW platforms; consider offline-capable apps for remote sites.
- Define approval, execution, and closure procedures, ensuring all stakeholders sign off.
- Emergency Preparedness
- Develop an Emergency Response Plan covering fire, spill, and medical incidents.
- Conduct quarterly drills, capture performance metrics, and update plans accordingly.
5. Performance Evaluation
- Internal Audits
- Rotate audit teams for impartial reviews.
- Document non-conformities, severity levels, and propose corrective actions in audit reports.
- Incident Investigation
- Apply 5 Whys or Fishbone Analysis for root-cause detection.
- Record actions in a CAPA register, assign owners, and verify effectiveness.
- Management Review
- Conduct biannual reviews covering audit outcomes, KPI trends, resource gaps, and stakeholder feedback.
- Document minutes, decisions, and accountability for follow-up actions.
6. Continual Improvement & Certification
- Corrective Action Plans (CAPA)
- Maintain a live CAPA register with progress tracking and closure verification.
- Pre‑Certification Audit
- Commission a mock audit to validate documentation and processes.
- Close minor findings before the formal assessment.
- Certification Audit
- Stage 1: Registrar reviews your OHSMS documentation remotely.
- Stage 2: On-site audit assesses implementation, interviews staff, and inspects facilities.
Ready to certify?
Contact us for end-to-end Stage 1 & 2 audit support.
Common Implementation Challenges & Solutions
Challenge Solution Diverse languages onsite Translate SOPs and training materials; use pictograms and video. Connectivity limitations Deploy offline-capable compliance apps for PTW and reporting. Resistance to change Launch a safety culture campaign highlighting employee benefits.
Partner with OH&S Experts
While this guide delivers a robust blueprint, our consultancy empowers you with hands-on expertise, region-specific insights, and proven tools:
- Turnkey ISO 45001 implementation from gap analysis to certification.
- Custom, multilingual training and workshops tailored to your sector.
- Digital templates and compliance platforms to streamline OHSMS.
Get started today:
Contact us for a free project scoping call and bespoke proposal.
Conclusion
Adopting ISO 45001 in UAE Free Zones transforms your safety management—from a regulatory obligation into a strategic asset that attracts clients, reduces risks, and elevates brand reputation. By following this detailed roadmap and leveraging specialized support, you’ll achieve certification faster and sustain continual improvement.
Don’t wait—secure your OH&S excellence now.
Contact us to begin your ISO 45001 journey.
