Your cart is currently empty!
Tag: Digital Safety Tools
-
Free H&S Risk Assessment Template: How to Use It for Workplace Safety
Ensuring a safe working environment isn’t just about ticking boxes—it’s about protecting your team, your reputation, and your bottom line. A well-structured H&S risk assessment template is the cornerstone of any proactive health and safety (H&S) programme. In this comprehensive guide, you’ll discover:
- Why a Risk Assessment Matters
- Key Legislative Requirements & Standards
- Anatomy of an H&S Risk Assessment Template
- Step-by-Step Instructions for Completion
- Using a Risk Matrix to Prioritise Hazards
- Implementing and Monitoring Control Measures
- Case Study: Real-World Application
- Common Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
- Digital Tools & Automation for Streamlined Assessments
- Embedding Safety Culture Across Your Organisation
- Measuring Success & Continuous Improvement
- Next Steps & How to Request Your Free Template
And if you’d like an editable, bespoke template you can adapt to your specific operations, simply contact us to request your free H&S risk assessment template today!
1. Why a Risk Assessment Matters
A risk assessment template is more than compliance paperwork—it’s your roadmap to:
- Protecting People: By identifying hazards such as slips, trips, machinery entanglement or chemical exposure, you can act before injuries occur.
- Reducing Costs: Preventing accidents saves on lost production, insurance premiums and legal fees.
- Ensuring Compliance: UK law mandates employers assess and control risks; a documented assessment demonstrates due diligence.
- Driving Continuous Improvement: Regular reviews encourage refinement of procedures, training and resource allocation.
2. Key Legislative Requirements & Standards
A robust H&S programme aligns with these critical frameworks:
- Health and Safety at Work etc. Act 1974: Primary UK legislation placing a duty on employers to safeguard employees’ health and safety.
- Management of Health and Safety at Work Regulations 1999: Requires suitable and sufficient risk assessments covering hazard identification, risk evaluation and control implementation.
- ISO 45001:2018: Global standard for Occupational Health & Safety Management Systems, promoting legal compliance and performance improvement.
- COSHH Regulations 2002: Governs the management of hazardous substances, including specific risk assessments for chemical exposure.
3. Anatomy of an H&S Risk Assessment Template
Every effective template guides you through these essential sections:
- Activity Description: Define the scope, for example “Forklift loading operation in warehouse Bay 3.”
- Hazard Identification: List specific hazards, such as unguarded moving parts or manual handling risks.
- Who Might Be Harmed: Identify affected groups—operators, maintenance staff, visitors.
- Risk Evaluation: Rate likelihood and severity on a simple 1–5 scale.
- Risk Score: Multiply likelihood by severity to prioritise hazards.
- Control Measures: Document existing controls (Guards, PPE, training) and propose additional measures.
- Priority & Action Owner: Assign each action a priority level, responsible person and deadline.
- Review Date: Schedule the next reassessment—at least annually or after any significant change.
- Notes & Comments: Capture observations, worker suggestions or follow-up items.
4. Step-by-Step Instructions for Completion
- Select and Describe the Activity
- Focus on highest-risk tasks such as machinery operation or chemical handling.
- Provide enough detail so reviewers understand the exact process.
- Walk the Process and Engage Staff
- Conduct a physical walkthrough.
- Interview front-line staff to uncover hidden hazards.
- Identify Hazards Precisely
- Replace generic terms with specifics (e.g., “unguarded rotating shafts on Press A”).
- Consider environmental factors like noise or temperature extremes.
- Evaluate Risk
- Assign a likelihood score (1 = Rare to 5 = Almost Certain).
- Assign a severity score (1 = Minor injury to 5 = Fatality).
- Calculate the Risk Score
- Multiply likelihood by severity to get a numerical score.
- Use colour codes or tiers (e.g., 1–6 = Low, 7–12 = Medium, 13–25 = High).
- Document Controls
- List existing measures first (e.g., guards, PPE).
- Propose new controls: engineering fixes, administrative updates, or training.
- Assign Actions and Deadlines
- Set realistic timeframes and responsibility, such as:
- Action: Install pressure-sensitive mat on press base
- Owner: Jamie Lee
- Deadline: 15 Aug 2025
- Set realistic timeframes and responsibility, such as:
- Review and Close Out
- Confirm actions are completed, update the template and reset the review cycle.
- Record evidence of completion, like photos or emails.
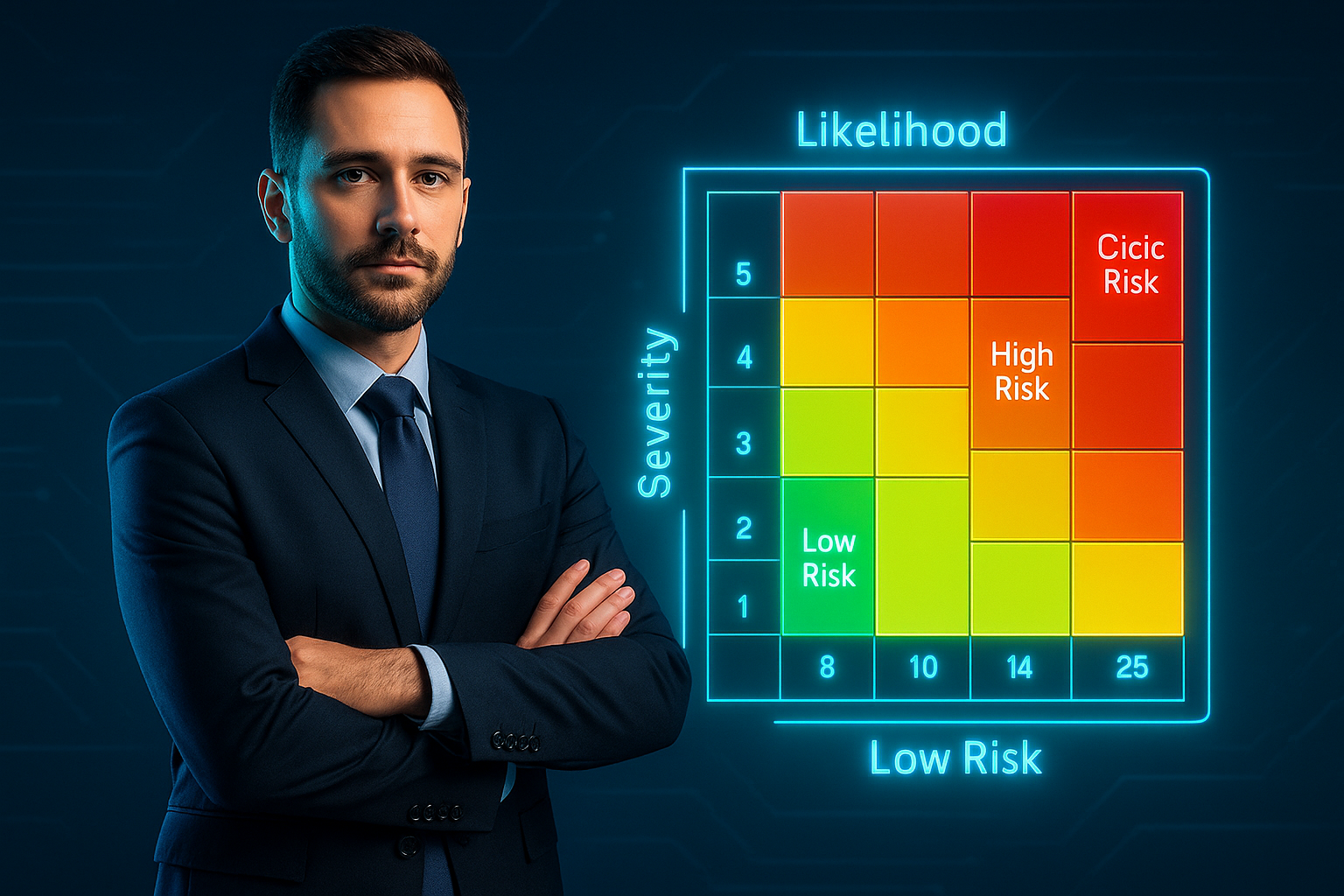
5. Using a Risk Matrix to Prioritise Hazards
A visual risk matrix enables quick identification of high-risk areas. For example, a simple 5×5 grid where:
- The vertical axis represents Likelihood (1–5)
- The horizontal axis represents Severity (1–5)
- Each cell is colour-coded: Green for Low, Amber for Medium, Red for High
Embed this matrix in your template or digital tool to auto-highlight critical items.
6. Implementing and Monitoring Control Measures
- Engineering Controls: Machine guards, interlocks, ventilation systems.
- Administrative Controls: Updated procedures, safety signage, shift rotations.
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Last line of defence—ensure fit, selection and training.
- Monitoring: Schedule monthly inspections, maintain a near-miss reporting system and hold regular review meetings with action owners.
Document all findings and follow up until each control is verified as effective.
7. Case Study: Real-World Application
Scenario: A manufacturing company faced frequent near misses at a stamping press.
Steps Taken:
- Identified unguarded moving parts and poor housekeeping.
- Rated risk as High (Likelihood 4 × Severity 4 = 16).
- Proposed controls: install fixed guards, implement floor-marking zones and weekly housekeeping checks.
- Assigned actions with deadlines and owners.
Outcome: Zero near misses over three months, an 8% reduction in insurance premiums and positive audit feedback from HSE inspectors.
8. Common Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
- Vague Hazard Entries: Always use precise descriptions (e.g., “oil spill near Packing Bay 2”).
- Skipping Worker Engagement: Conduct short workshops or toolbox talks before completing the form.
- One-Time Assessments: Schedule reassessments at least annually and after any incident.
- Over-Engineering Controls: Balance cost versus benefit—sometimes signage or training suffices.
- Lack of Follow-Up: Use digital reminders or calendar alerts to track and close out actions.
9. Digital Tools & Automation for Streamlined Assessments
- Mobile Inspection Apps: Capture data, photos and trigger reminders on the go.
- Cloud-Hosted Risk Registers: Centralise assessments, track trends and generate dashboards.
- Automated Reminders: Emails triggered when review dates or deadlines approach.
- Analytics & Reporting: Quickly identify top hazards, overdue actions and training gaps.
Ask us about integrating these tools when you contact us.
10. Embedding Safety Culture Across Your Organisation
- Leadership Involvement: Have senior management review high-risk items quarterly.
- Continuous Communication: Share lessons learned in newsletters and meetings.
- Recognition Programs: Reward teams for proactive hazard reporting and action-closure rates.
- Training & Development: Refresh assessors on best practices and emerging risks, such as ergonomic hazards or remote-work stress.
11. Measuring Success & Continuous Improvement
Track these key performance indicators (KPIs):
- Number of assessments completed
- Actions closed versus overdue
- Incident and near-miss trends
- Audit findings and compliance scores
- Employee safety perception survey results
Review these metrics quarterly to ensure your H&S programme evolves effectively.
12. Next Steps & How to Request Your Free Template
A tailored, editable H&S risk assessment template simplifies the start of your safety programme. To request yours:
- Visit our Contact Us page.
- Tell us about your organisation and primary activities.
- Receive your bespoke, fully editable template within one business day—no cost, no obligation.
Start your journey to a safer workplace today. Complete your first assessment, close out actions, and watch your incident rates—and costs—fall.