Your cart is currently empty!
Tag: risk management software
-
Ultimate Guide to Conducting a Workplace Risk Assessment
Welcome to the definitive resource for workplace risk assessment, designed to empower safety managers, HR leaders, and business owners with the tools and insights needed to transform risk management from a compliance obligation into a competitive advantage. In today’s fast-paced industrial and commercial environments, proactive hazard identification and mitigation are critical for reducing incidents, minimizing downtime, and protecting both people and profits.
In this guide, you will discover:
- Actionable step-by-step processes using our customizable risk assessment checklist and risk assessment template to ensure no hazard is overlooked.
- Data-driven strategies for quantifying risk with a color-coded risk matrix, scoring methodology, and performance metrics that drive measurable safety improvements.
- Best practices for OSHA & HSE compliance and international standards (ISO 31000, ISO 45001), including how to integrate requirements into your existing management systems.
- Advanced techniques—from IoT-enabled hazard detection to predictive analytics—that elevate your program and future-proof your operations.
By the end of this guide, you’ll have a comprehensive risk register framework, practical engineering and administrative control recommendations, and a blueprint for building a dynamic, continuous improvement process—backed by real-world case studies demonstrating substantial ROI. Let’s get started on creating a safer, more resilient workplace.
What Is a Workplace Risk Assessment?
A workplace risk assessment is a structured risk management process for:
- Identifying hazards across operations, equipment, and workflows.
- Assessing how likely each hazard is to cause harm and the severity of potential injuries.
- Implementing control measures prioritized by impact and cost-effectiveness.
- Documenting every decision to provide an audit trail and support continuous improvement.
This proactive approach fosters a safety-first culture, turning compliance into a competitive advantage.
Keywords: workplace risk assessment, risk management process, hazard identification checklist
Business Benefits & ROI of Risk Assessments
Investing in risk assessments delivers measurable returns:
- Reduced Incident Costs: Companies can save $3–$6 for every $1 spent on safety programs by preventing injuries and downtime.
- Lower Insurance Premiums: Demonstrating an effective safety program can earn you discounts of 5–15% on workers’ compensation rates.
- Operational Continuity: Fewer accidents mean less disruption—maintaining productivity and meeting project deadlines.
- Enhanced Reputation: Clients and investors prioritize partners with robust safety records, strengthening your brand and winning bids.
Keywords: safety ROI, incident cost savings, insurance premium reduction
Regulatory Landscape & Industry Standards
Understanding requirements in your jurisdiction is critical:
Region Legislation/Standard Key Focus UK Health and Safety at Work etc. Act 1974; ISO 31000 Systematic risk management, employer duties US OSHA Act; ANSI Z10 General industry standards, management systems EU Framework Directive 89/391/EEC; ISO 45001 Worker involvement, continual improvement Action Point: Map local laws to global standards (ISO) to create a unified risk framework.
Keywords: OSHA compliance, ISO 45001, HSE regulations
5-Step Risk Assessment Process Explained
Step 1: Identify Hazards with a Risk Assessment Checklist
Objective: Compile a complete inventory of potential hazards across physical, chemical, biological, ergonomic, and psychosocial domains.
- Site Audits: Perform day and night inspections; use digital apps to log photos, GPS coordinates, and time stamps.
- Task Analysis Workshops: Engage cross-functional teams to map workflows, pinpointing high-risk touchpoints.
- Data Analysis: Leverage historical incident, near-miss, and insurance claim data to reveal hidden patterns.
Step 2: Determine Who’s at Risk & Potential Injuries
Objective: Clearly define affected populations and characterize injury types for targeted controls.
- Stakeholder Mapping: List all individuals—employees, contractors, visitors, maintenance technicians.
- Injury Taxonomy: Categorize hazards by likely injuries: lacerations, MSDs, respiratory issues, hearing loss, psychological stress.
Step 3: Evaluate Risk Severity & Likelihood
Objective: Assign quantifiable scores to prioritize control measures effectively.
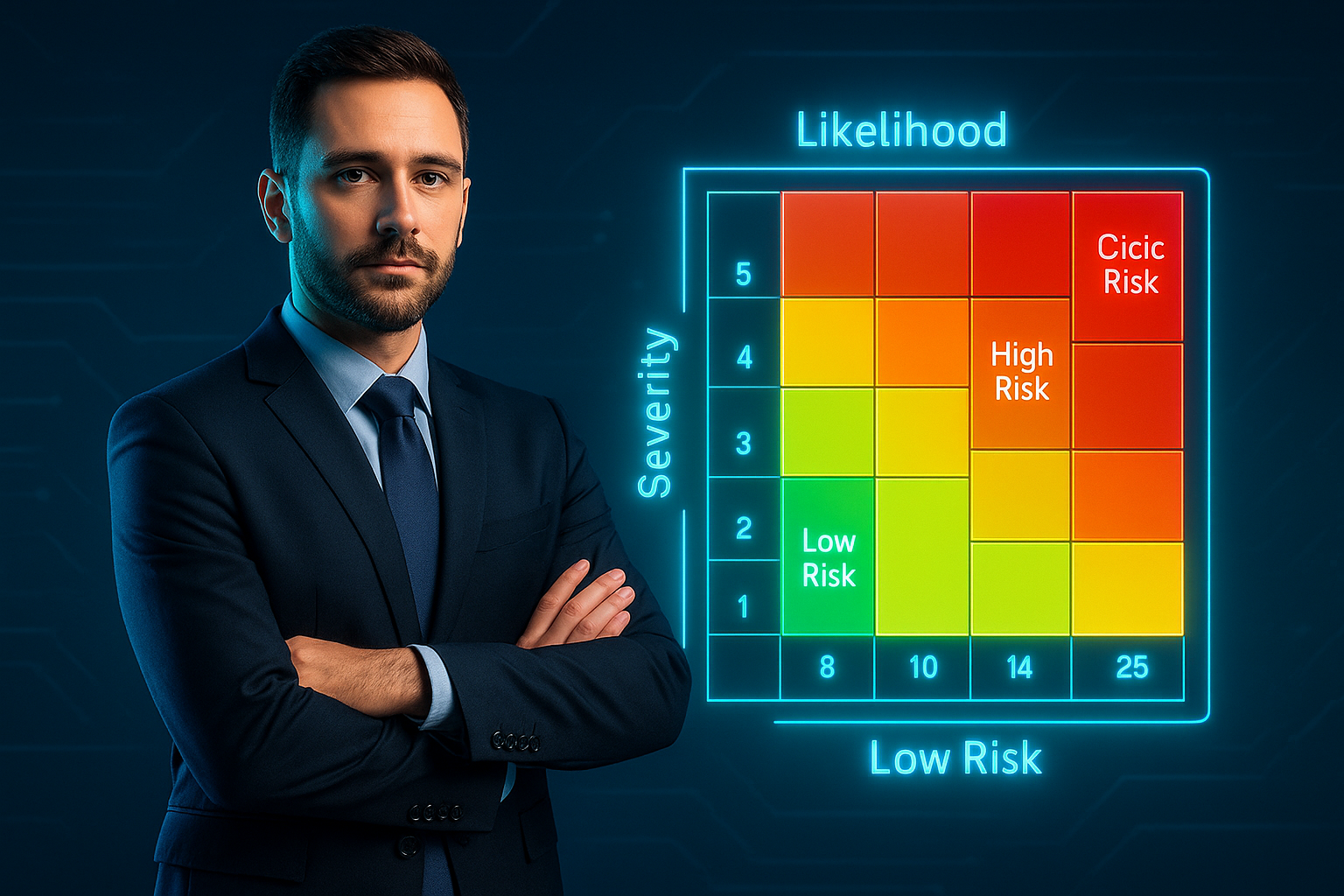
- 5×5 Risk Matrix: Define clear scoring criteria for each severity and likelihood category, ensuring consistency across teams.
- Weighted Scoring: Apply weights for critical processes (e.g., production line vs. office area) to focus on business-critical zones.
Risk Score Formula:
Risk Score = Severity Rating × Likelihood Rating
• Severity and Likelihood are each rated 1 (lowest) to 5 (highest).
• Scores range from 1–25, grouped into risk bands.Color-Coded Risk Matrix
Risk Bands Explanation:
- Low Risk (1–7): Green — acceptable, monitor periodically.
- Medium Risk (8–14): Yellow — plan corrective actions within 30–60 days.
- High Risk (15–19): Orange — implement controls immediately.
- Critical Risk (20–25): Red — stop operation and apply urgent mitigation.
Step 4: Implement Controls Using the Hierarchy of Controls
Objective: Eliminate or reduce risks in order of effectiveness.
- Elimination/Substitution: Remove the hazard or replace it with a less hazardous option—e.g., switch to water-based adhesives.
- Engineering Controls: Install machine guards, ventilation hoods, or noise dampening barriers.
- Administrative Controls: Develop SOPs, conduct regular training sessions, and schedule job rotations to minimize exposure.
- PPE: Issue certified gloves, respirators, and eyewear; ensure fit-testing and compliance monitoring.
Step 5: Monitor, Review & Update Your Risk Register
Objective: Maintain momentum and adapt to evolving risks.
- Automated Alerts: Schedule periodic reviews (monthly, quarterly) based on control criticality.
- KPI Tracking: Monitor metrics like Incident Frequency Rate (IFR), average time to close risk items, and employee engagement scores.
- Continuous Feedback Loop: Solicit suggestions via safety committees and anonymous reporting channels.
Common Industry-Specific Hazards & Mitigation
Industry Hazard Category Specific Risks Top Mitigations Manufacturing Mechanical, Noise Machine entanglement, hearing loss Guarding systems, hearing conservation Construction Falls, Struck-by Heights, falling debris Fall arrest harness, debris netting Healthcare Biological, Sharps Pathogen exposure, needle-stick injuries Isolation rooms, sharps disposal programs Office Ergonomic, IAQ Repetitive strain, poor air filtration Adjustable workstations, HVAC upgrades Warehousing Material Handling Manual lifting, forklift collisions Lift-assist devices, aisle marking systems Keywords: industry-specific hazards, fall arrest, hearing conservation program
Tools, Templates & Software Integrations
- Risk Assessment Template (Excel/Word): Pre-built tables with dropdowns for scoring and status tracking. Contact us if you want one build for you.
- Digital Inspection Apps: Make safety digital with easy to use integrated apps for inspection to keep records alive and compliance 100%. Contact us if you want one build for you.
- Risk Management Systems: Have an onsite/offsite health and safety management system to keep on top of compliance. Contact us if you want one build for you.
Performance Metrics & KPIs
Track these to measure program effectiveness:
Metric Calculation Target Benchmark Incident Frequency Rate (IFR) (Number of incidents × 200,000) ÷ Hours worked <2.0 across industries Near-Miss Reporting Rate Near-misses reported ÷ total work hours Increasing trend month-over-month Control Closure Time Average days to implement controls <30 days Training Completion Rate Employees trained ÷ total assigned 100% Contact us if you want a KPI system build for you
Case Study: Company X’s Risk Reduction Success
Background: A 120-employee electrical manufacturer faced a surge in hand and back injuries.
- Hazard Identification: Used wearable sensors to detect repetitive motions.
- Risk Evaluation: Prioritized manual handling tasks with the highest RSI rates.
- Controls: Installed lift-assist arms (engineering) and introduced micro-break protocols (administrative).
- Review: Monthly dashboards showed a 50% drop in injury claims.
Result: Over 6 months, total incident costs decreased by $150,000, and OSHA recordable injuries fell by 60%.
FAQ: Risk Assessment Best Practices
Q1: How often should I update my risk assessment?
A: At a minimum, annually—or immediately after any significant change such as new equipment, processes, or after a reportable incident.Q2: Can small businesses conduct risk assessments without dedicated software?
A: Yes—start with our free Excel template and hazard checklist, then scale to digital platforms as your program matures.Q3: What’s the most common mistake in risk assessments?
A: Relying solely on PPE. Always prioritize higher-level controls (elimination, substitution, engineering) before PPE.Q4: How do I engage employees in the risk assessment process?
A: Create safety committees, hold regular toolbox talks, and incentivize near-miss reporting with recognition programs.
Key Takeaways & Next Steps
- Contact us if you need a simple ready-to-use template to get your risk assessment project kick-started
- Implement the 5-step risk assessment process with rigorous documentation.
- Leverage custom build Health and Safety management system from Safe-comply for automation and analytics.
- Monitor key safety KPIs and foster employee involvement for a thriving safety culture.
Ready to elevate your safety program?
Contact Us for a free consultation